Instead of directly working with Cloud Manager’s git repository, customers can work with their own git repository or multiple own git repositories. In these cases, an automated synchronization process should be set up to ensure that Cloud Manager’s git repository is always kept up-to-date. With an automation in place, every push to a customer-owned git repository can be automatically forwarded to Cloud Manager’s git repository.
Prerequisites:
To complete this tutorial, you need to have following things
- Azure DevOps Personal Access Token
- Adobe Cloud Manager Access Repo Info
- Setup Azure pipeline
Steps:
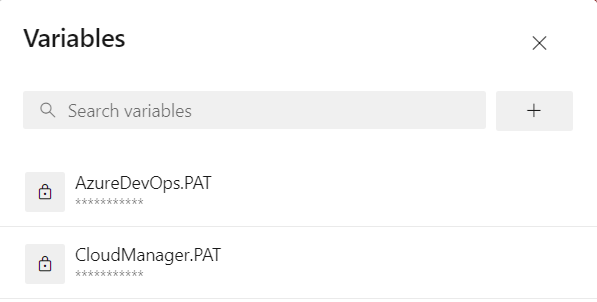
- Create new Azure pipeline and add pipeline variables as secret variables
a. CloudManager.PAT with value as your Cloud Manager PAT
b. AzureDevOps.PAT with value as your Azure DevOps PAT
2. Add a Powershell task

3. Refer the below script
# Starter pipeline# Start with a minimal pipeline that you can customize to build and deploy your code.# Add steps that build, run tests, deploy, and more:# https://aka.ms/yaml trigger:- mainpool:vmImage: ubuntu-lateststeps:- task: PowerShell@2inputs:targetType: 'inline'script: |# Write your PowerShell commands here.Write-Host ' - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -'Write-Host ' Reflect Azure Devops repo changes to Cloud Manager repo'Write Host ' - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - '$stageDir = '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)' | Split-Path$githubDir = $stageDir +"/"+"gitHub"$destination = $githubDir +"/"+"<azure-repo-name>.git"#please provide your username$alias = '<userName>:'+ "$(CloudManager.PAT)"#Please make sure, you remove https from azure-repo-clone-url#Example: https://$(AzureDevOps.PAT)@dev.azure.com/santoshsai/_git/MySite$sourceURL = https://$(AzureDevOps.PAT)@<azure-repo-clone-url>#Please make sure, you remove https from cloud-repo-clone-url#Example: @git.cloudmanager.adobe.com/xyzgrouppartnersandbox/MySite/$destURL = 'https://' + $alias + '@<github-repo-clone-url>'#Check if the parent directory exists and deleteif((Test-Path -path $githubDir)){Remove-Item -Path $githubDir -Recurse -force}if(!(Test-Path -path $githubDir)){New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $githubDirSet-Location $githubDirgit clone --mirror $sourceURL} else {Write-Host "The given folder path $githubDir already exists";}Set-Location $destinationWrite-Output '*****Git removing remote origin****'git remote rm originWrite-Output '*****Git remote add****'git remote add --mirror=fetch origin $destURLWrite-Output '*****Git fetch origin****'git fetch $sourceURLWrite-Output '*****Git push to Cloud Manager****'git push -f origin --allWrite-Output '**Azure Devops repo synced with Cloud Manager repo**'Set-Location $stageDirif((Test-Path -path $githubDir)) {Remove-Item -Path $githubDir -Recurse -force}
Optional Step:
Specify events that trigger pipelines
Use triggers to run a pipeline automatically. Azure Pipelines supports many types of triggers. Based on your pipeline’s type
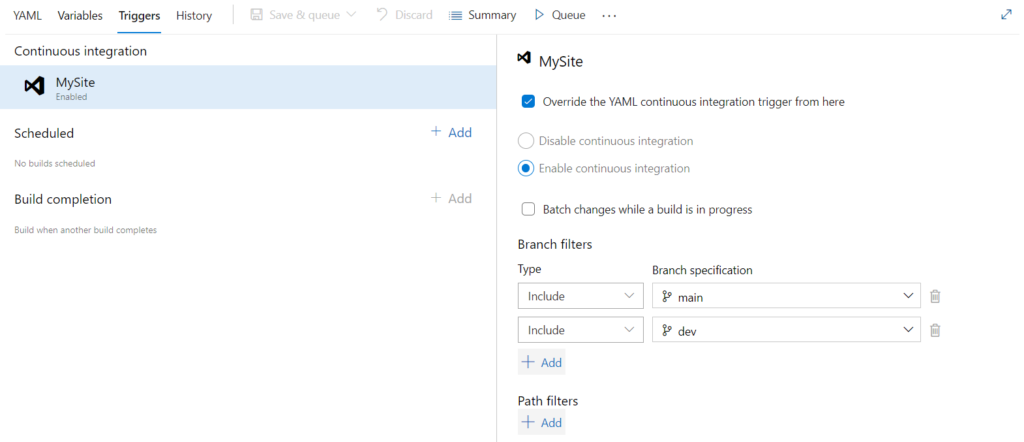
Now, whenever push performs on main or dev branch the pipeline will trigger automatically and perform the action as per script.
Hope you enjoyed this article, Thank you for your attention!